Business
-
Business
THE BIG PICTURE: Infrastructure
Aging infrastructure ranks at the top of the U.S. electric power sector’s concerns, flanked by the exorbitant investment needed to keep the system in good repair.
-
Environmental
South Korea Enacts Cap-and-Trade Program
The Republic of Korea’s National Assembly on May 2 passed legislation that will mandate cuts in greenhouse gases (GHGs) starting in 2015. The Act on Allocation and Trading of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Allowances passed with a near unanimous vote of 140-0, with three abstentions. It follows the country’s voluntary GHG emissions reduction target of 30% […]
-
Business
POWER Digest (July 2012)
UK Unveils Draft Energy Reform Bill. A draft energy bill unveiled by the UK’s Department of Energy and Climate Change on May 22 seeks to attract £110 billion ($168 billion) of investment to build new nuclear, renewables, and carbon capture and storage (CCS) plants to replace nearly a fifth of the country’s total power capacity, […]
-
Hydro
FERC Rule 1000: What Does It Mean?
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) has the responsibility for ensuring just and reasonable rates and preventing undue discrimination by public utility transmission providers. Last year FERC defined a new framework for public utilities and regional transmission organizations planning new transmission networks. The framework is provided in Order No. 1000—Transmission Planning and Allocation by Transmission Owning and Operating Public Utilities. The Final Rule was issued on July 21, 2011, and reaffirmed by Order No. 1000-A on May 17, 2012.
-
Legal & Regulatory
When Successful Procurement Policies Fail
California is approaching a tipping point with respect to the near-term economic viability of existing non-utility generation. The procurement policies and practices implemented in response to the statewide energy crisis over a decade ago have evolved into market conditions that do not offer “uncontracted” existing resources with sufficient and stable enough revenue streams to recover going-forward costs. Continued adherence to these policies will subject such resources to an increasing risk of economic retirement, threatening long-term reliability and potentially costing electric consumers billions of dollars.
-
Coal
Power in India: Opportunities and Challenges in a Fast-Growing Market
India’s long-term annual economic growth rate is projected at over 7%, and the country is investing in its hydroelectric, nuclear, and renewable resources. However, the primary fuel used to produce electricity remains coal, and the government has ambitious plans to significantly increase coal-fired capacity. Those plans have been challenged by a number of unexpected factors that threaten to stifle India’s economic growth. India’s long-term annual economic growth rate is projected at over 7%, and the country is investing in its hydroelectric, nuclear, and renewable resources. However, the primary fuel used to produce electricity remains coal, and the government has ambitious plans to significantly increase coal-fired capacity. Those plans have been challenged by a number of unexpected factors that threaten to stifle India’s economic growth.
-
Business
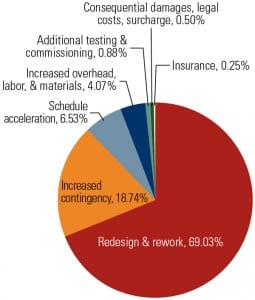
Allocating Project Risk
Power generators typically allocate construction risks through the process of aversion. Owners have a tendency to shift risk to a project’s primary contractor, who in turn pushes it to lower-tier parties in the contracting arrangement. Research by the Construction Industry Institute has found that there are more equitable ways to allocate project risk.
-
Hydro
Utility Perspectives on Ramping Up Renewable Power
Panelists at ELECTRIC POWER discussed how U.S. utilities choose renewable power generation technologies based on their geographic locations, state requirements, economics, and other criteria—including reliability and federal regulations.
-
Coal
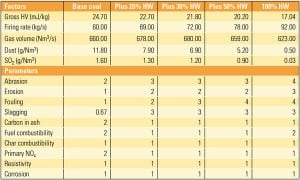
New Technologies Advance Biomass for Power Generation
As U.S. utilities seek to increase the percentage of carbon-neutral biomass used in their generation portfolios, they must deal with a number of complex challenges unique to this fuel source. Several breakthrough technologies are poised to help promote greater use of biomaterials.
-
Environmental
Fracking Guidelines Expand as Technology Evolves
New federal regulations promise to change the fracking landscape in the coming years, perhaps substantially. But technology may be running ahead of the law, as improvements in the fracking process threaten to make some of the new rules unnecessary.